Important:This document may not represent best practices for current development. Links to downloads and other resources may no longer be valid.
- Read Mac Filesystem On Windows
- Best Filesystem For Mac Linux And Windows
- Linux Filesystem Commands
- Filesystem For Linux And Mac Operating System
- Linux File System
- Filesystem For Linux And Mac Os
- What’s the best filesystem to use on OS X, Linux and Windows? You mean as in what filesystem rules them all, like the best single filesystem that works on all of them? Simple exFAT Not because it’s the best filesystem, far from it, but because th.
- Creating filesystem in a partition: Creating filesystem in a RAW disk is possible however its advice.
- The exfat driver for macos is not as full-featured as on windows, and on mac the drive often gets the dirty flag set, as result you might need to to wait for hours (on multi-TB drives) the next time you plug it it because fsckexfat has to finish checking it. The linux driver for exfat is.
- The filesystem was cloned, so I am trying to find any configurational file which contains the string with MAC address. What file is usually red by ifconfig to display network interfaces information? Networking configuration ifconfig.
The following sections discuss the file systems supported by OS X and the impact they can have on application performance.
I have an external drive hooked up to my Mac, and I'm trying to determine things like, e.g., is this HFS or FAT, is it 32-bit or 64-bit, etc. It seems like there should be some trivial command that gives me this info, but I can't seem to find one.
Supported File Systems
Read Mac Filesystem On Windows
OS X supports a variety of file systems and volume formats, including those listed in Table 1. Although the primary volume format is HFS Plus, OS X can also boot from a disk formatted with the UFS file system. Future versions of OS X may be bootable with other volume formats as well.
File System | Description |
|---|---|
HFS | Mac OS Standard file system. Standard Macintosh file system for older versions of Mac OS. |
HFS Plus | Mac OS Extended file system. Standard Macintosh file system for OS X. |
UFS | Unix File System. A variant of the BSD “Fast File System.” |
WebDAV | Used for directly accessing files on the web. For example, iDisk uses WebDAV for accessing files. |
UDF | Universal Disk Format. The standard file system for all forms of DVD media (video, ROM, RAM and RW) and some writable CD formats. |
FAT | The MS-DOS file system, with 16- and 32-bit variants. |
SMB/CIFS | Used for sharing files with Microsoft Windows SMB file servers. Install Mac OS X Yosemite on VMware, and it is the 11th major release of Mac, Apple company. Therefore, this version of Mac OS X Yosemite is 10.10 and it was the old version of macOS operating system among the other operating systems. VMware Fusion: Powerfully Simple Virtual Machines for Mac. VMware Fusion Pro and VMware Fusion Player Desktop Hypervisors give Mac users the power to run Windows on Mac along with hundreds of other operating systems, containers or Kubernetes clusters, side by side with Mac applications, without rebooting. Fusion products are simple enough for home users and powerful enough for IT. Vmware for mac lion. |
AFP | How to network macs. AppleTalk Filing Protocol. The primary network file system for all versions of Mac OS. |
NFS | Network File System. A commonly-used BSD file sharing standard. OS X supports NFSv2 and NFSv3 over TCP and UDP. |
FTP | A file system wrapper for the standard Internet File Transfer Protocol. |
Best Filesystem For Mac Linux And Windows
Accessing File-System Data
Linux Filesystem Commands
Every file system stores metadata about the files in the file system. This metadata describes the file but is not part of the file itself. The metadata for a file can include attributes such as Mac OS file type information, BSD-style file access permissions, and creation and modification dates. Because of the differences in how file systems store this data, accessing metadata can be a potentially expensive operation on some file systems.
It’s important to realize that if a piece of data is not immediately present in the file system, that information might have to be calculated. Retrieving file-system information is a time-consuming operation as it is, but if the information must be calculated or read separately from disk, it becomes even more time-consuming. The valence of a directory—the number of items in that directory—is a typical example of information that must be calculated on most file systems.
When calling file-system routines, you should always carefully consider what information you actually need and request only that information. For example, a single call to PBGetCatInfoSync returns Finder file type information from a file or folder. On HFS and HFS Plus file systems, the penalty for retrieving this metadata is minimal because it is stored in the file’s catalog node and read into memory along with the file name. However, on other file systems, this data may have to be read separately, incurring another read operation. Instead of PBGetCatInfoSync, you should have used FSGetCatalogInfo or PBGetCatalogInfoSync and specified exactly which pieces of information you wanted.
Filesystem For Linux And Mac Operating System
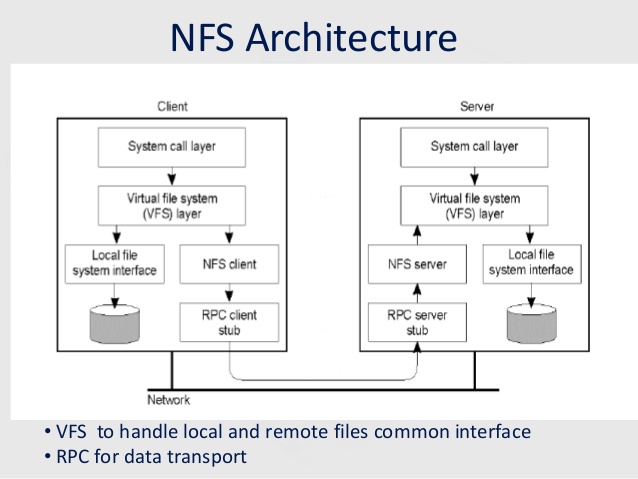
Linux File System
Filesystem For Linux And Mac Os
Copyright © 2003, 2014 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Updated: 2014-03-10
